Завдання №1.
Прочитайте і перекладіть текст.
The Control of Weeds and Plant Diseases.
In crop production the control of weeds, diseases and pests is
essential to obtain high yields. All three may be controlled by sound farm
practices. These include the choice of clean seed and the growing of varieties
of crop which can resist disease. They also include careful cultivation, both
presowing and post-sowing, and the use of chemicals.
Weeds reduce crop yields
on account of the fact that they compete with crops for water, soil nutrients
and light. They also make harvesting difficult. Most weeds are aggressive and
invasive, they grow guickly and spread far, and so are difficult to get rid of.
One recommended way of eradicating many persistent weeds is first to plough up
the roots and underground parts of the plant. Then the soil may be cultivated
lightly, or rotavated, on one or more occasions after the first ploughing.
The principal reason for
cultivating the soil is to kill weeds. Weeds may also be killed by means of
chemicals which have the collective name of herbicides. Weed-killers are of two
basic types: selective and non-selective.
The former remove
certain weeds from certain crops. For rice we can spray the herbicide 2:4-D or
MCPA over the whole crop at low concentrations (1/2 –
Plant diseases are
caused by organisms which use the crop plant as a host. These are mainly
micro-organisms e.g. fungi, bacteria and viruses.
These parasitic
micro-organisms live off the food nutrients in the tissue cells of the plant or
a part of it is damaged and killed. Micro-organisms are bacteria.
Wind, water, diseased
plants, cuttings and tubers, animals, men and insects are some of the means
whereby disease is disseminated.
It is very difficult to
kill the fungi and bacteria, or to make the virus which is inside the host
plant inactive. But the evolution of plant varieties which can resist disease
has completely changed methods of disease control.
A number of varieties
have been evolved and now available to farmers.
So the control of plant
diseases has increasingly become a matter of prevention.
Fungi, which attack the
aerial parts of the crop, can be controlled by means of fungicides. These are
sprayed or dusted on to the plant surfaces.
They should be applied
before the plant is seriously damaged. In any case, it is necessary to examine
crops frequently for signs of disease.
Soil-borne diseases are
much more difficult to control. There are various ways of treating the soil.
One way is to use chemicals that easily change into a gas or vapour, which
enter the soil and kill the harmful organisms. The soil is covered with a
polythene sheet and the volatile chemical is injected into the soil. After
about 24 hours the sheet is removed and the soil is allowed to air for a few
days before use.
Завдання № 2.
Додайте слово або фразу з тексту , щоб закінчити твердження , що показує чи вірно ви зрозуміли текст .Зверніть увагу на те , що крапкова лінія потребує фразу , а пряма - слово .Номер указує пропозицію в тексті .
a) Weeds , dieseases and
pests may be controled by … (2)
b) Sound farm practices
include the choice of clean seed and … (3)
c) Most weeds grow quickly
and spread far .They are ___and___
(7)Agrassive and invasive weeds are
difficult …… .
d) We can spray rice with ……(14)
e) Selective weed – killers
remove … (13)All weeds will be removed from all crops by …. (16)
f)
Plant diseases are caused by micro-organisms such as ….(20) Fungi ,
bakteria and viruses cause plant diseases by using …..
Завдання № 3.
Перефразуйте.
Перепишіть твердження , використовуючи слова і конструкції з
тексту.
1. Weeds which grow quickly and spread far are difficult to get
rid of .
2. A way which is
frequently advised to eradicate weeds which last a long time is to plough first
and than cultivate lightly.
3. Chemicals which remove
certain weeds from certain crops are used in rice cultivation , when they are
sprayed over the whole crop at low concentrations.
4. Organism which are
microscopic in size and use the crop plant as the ‘host’ are frequently the
cause of a whole crop being killed .
Завдання № 4. Визначення
й опис хвороб .
Хвороби рослин
можуть визначатися їхньою назвою й організмом , що викликає це захворювання.
Example
Crop Name of disease Causal organism
Rice blast fungus:Piricularia
oryzae
Ми можемо сформулювати визначення захворювань такими засобами :
Blast in rice is fungus
disease (which is) caused by the organism Piricularia
oryzae
The fungus organism Piricularia oryzae causes /is the cause
of blast rice.
Piricularia oryzae is a fungul organism which causes
blast in rice.
Сформулюйте визначення захворювань рослин
за зразком, даному вище.
|
Crop |
Name of disease
|
Causal organism |
|
1.Maize |
Smut |
Fungus:Ustilago zeae |
|
2.Groundnuts |
Rosette disease |
Virus |
|
3.Tomatoes |
Bakteria wilt |
Bakteria:Pseudomonas solanaceum |
|
4.Bean |
Anthracnose |
Fungus |
Завдання
№5.
Дати опис симптомів окремих захворювань
рослин .
Example:
Crop Name of Causal organism Symptoms
disease
Rice blast fungus:Piricularia Brown
longitudinal spots on
Oryzae ieaves.Spots on stem and grain
Darker in colour.
1.Blast in rice is a
fungus disease caused by the organism
Piricularia oryzae.Brown longitudinal spots apper on the leaves.The spots on the stem and grain are darker in
colour.
2.The fungul organism Piricularia oryzaeis the cause of blast
in rice.Brown longitudinal spots can be
seenon the leaves.The spots on the stem
and grain are darker in colour.
Використовуючи інформацію, запропоновану
нижче, додайте до визначень захворювань опису симптомів цих захворювань за
зразком даному вище. Де необхідно, додайте такі слова:
a)definite and indefinite articles;
b)forms of the verb be and apper,can be seen;
c)and
I
|
Identification |
Discription
|
||
|
Crop |
Name of disease |
Causal organism |
Symptoms |
|
1.Maize |
Smut |
Fungus:Ustilago zeae |
Soft tumours on all parts of plant, mostly cob. Tumours, when mature,
split and release black dusty mass of spores. |
|
2.Tomatoes |
Bakterial wilt |
Bacteria:Pseudomonas solanacerum |
Lower leaves wilt,and eventually
die. |
|
3.Groundnuts |
Rosette disease |
Virus |
Circular spots on both sides of leaves.Spots
on upper surface dark brown with yellow halo. |
|
4.Bean |
Anthracnose |
Fungus |
Red or black spots and a pinkish
mold on ponds or seeds. |
Завдання № 6.
Після визначення захворювання і його опису, ми можемо сформулювати рекомендації контрольних індивідуальних мір або засобів запобігання цих захворювань .
e.g
|
Crop |
Name of disease |
Causal Organism |
Symptoms |
Control measures |
|
Rice |
Blast |
Fungus:Piricularia oryzae |
Brown longitudinal spots on leaves.Spots on stem and grain darker in
colour. |
Spray with 1% |
Ми можемо висловити рекомендації різноманітними засобами :
As a
control measures ,the crop should be sprayed with 1%
Bordeaux mixture.
In
addition ,|Alternatively , to avoid the
disease ,resistant crop varieties should be grown .
2.One
control mesures is to spray with 1% Bordeaux mixture .In addition |
Alternatively
,
resistant crop varieties should be grown .
Вивчите дану
таблицю і сформулюйте визначення , опис хвороби і рекомендації по її контролю
або заходам для запобігання її.
e.g.
Blast in rice isa fungus disease caused by the organism Piricularia oryzae.In this disease brown
longitudinal spots apper on the leaves. The spots on the stem and
Grain are darker in colour . As a
control measure the crop can be sprayed with 1 % Bordeaux mixture. To avoid
the disease ,resistant crop varieties
should be grown.
|
Crop |
Name of disease |
Causal organism |
Symptoms |
Control measures |
|
Maize |
Smut |
Fungus:Ustilago zeae |
Soft tumours on all parts of
plant , mostly cob. |
Practice crop rotaitoin and
sanitaition.Or, grow resistant varieties. |
|
Tomatoes |
Bacterial wilt |
Bacteria:Pseudomonas solanacerum |
Lower leaves wilt , and
eventually die. |
Spray 1% |
|
Ground nuts |
Rosette disease |
Virus |
Circular spots on both sides of
leaves .Spots oh upper surface dark brown with yellow halo. |
Plant seeds early and close.Also
, use clean seed,and uproot and burn infected plants. |
|
Bean |
Anthrocnose |
Fungus |
Red or black spots and a pinkish
mold on ponds and seeds. |
Avoid working around wet plants,
remove affected plants. |
Завдання №7.
Прочитайте та перекладіть текст.
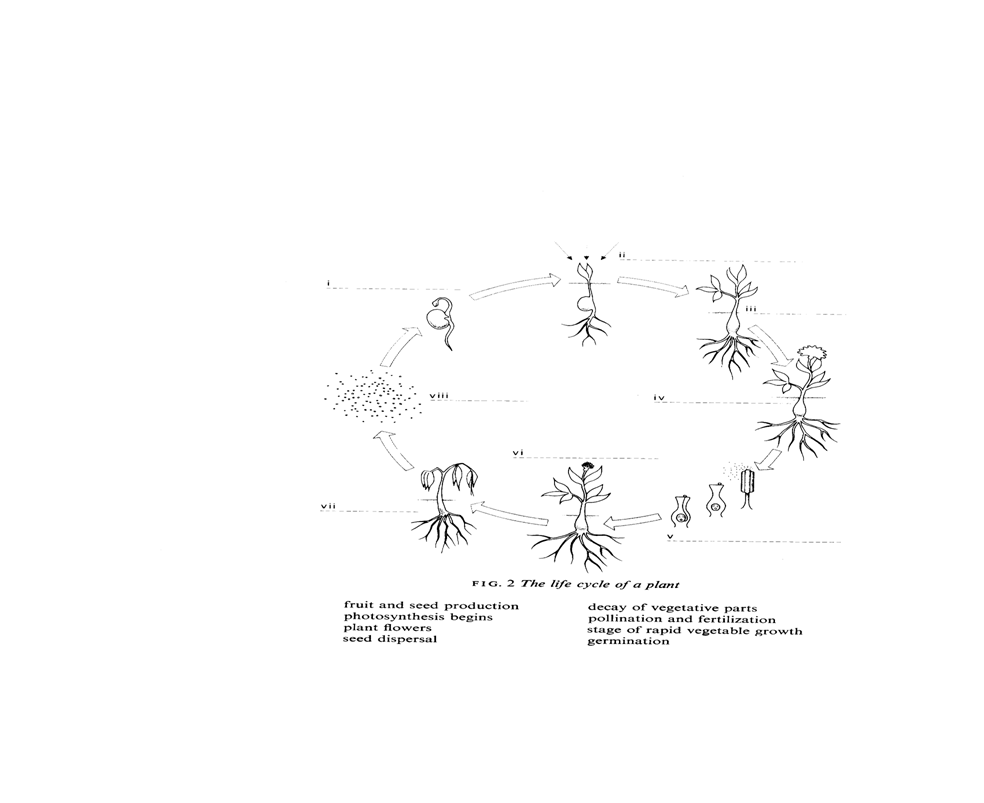
Тhe life cycle of a
plant .
Тhe life cycle of a
plant can be divided into several stages . the first stage is germination . seeds remain dormant , or in
a resting state , if they are kept cool or dry . when the amount of moisture
and the temperature level are right , the seeds germinate and starts growing .
Сertain conditions are
necessary for this to happen . an essential condition is the seeds must be
alive . sometimes seeds are dried at a temperature which is too high .
Оther condition
for germination concern the amount of
moisture in the soil . if dry seeds are planted in a dry soil , they will not
germinate until in rains . on the other
hand , if there is too much water in the
soil , the seeds will not germinate either . this is because wet soils remain
cold for a longer period of time than drier , well - drained soils .
dormant seeds require very little oxygen in order to stay alive , but when they
start to germinate they require more .
In the first stage of
germination the primary root , or radicle emerges .then the stem pushes its way
upward until it appears above the surface of the soil .at the same time the
root system grows downward , and begins
to spread through the soil .in early stages the development of seedlings
depends entirely on the foodstore in the seed
but as soon as the first leaves are produced , it is able to manufacture
food for itself . The seedlings begins photosynthesis .
When the plant is mature
enough , it flowers , and when this happens
pollination and fertilization are ready
to take place . In the process of pollination the pollen is carried by wind
Or insects from the
stamens to the stigma of the carpel .
Завдання № 8.
Додайте слова або фрази з тексту, щоб закінчити твердження, що показує вірно або ні ви зрозуміли текст. Зверніть увагу на те, що крапкова лінія
потребує фразу, а пряма лінія-слово. Номер указує пропозицію в тексті.
1.
If seeds are kept cool and dry they remain ________ .(3)
Seeds
germinate when ……….. .(4)
2.
Sometimes the temperature is ……….. when seeds are dried.(7)
As a result, the seeds _______ .(9)
3.
Dry seeds will not germinate if they are planted in ………. .(11)
If the soil is too _______ the seeds will
not _______ .( )
4.
Wet soils ……… longer than drier, well-drained soils.(13)
in order to ……. dormant seeds require very
little ______ .(16)
Завдання № 9.
Перепишіть пропозиції, замінюючи слова, виділені
курсивом, вираженнями з тексту, що мають те ж значення.
1. The seed start
growing when there is enough air or water and the temperature is right.
2. A seed will only
germinate when there is enough air in the soil.
3. As soon as the stem and
leaves appear above the surface of the soil, they begin to manufacture food.
4. The process of carrying the pollen to the stigma is brought about by
wind or insects.
Завдання № 10.
Визначення процесу.
Процеси визначаються тим, що відбувається
протягом їхньої діяльності.
e.g.
name of process: photosynthesis
identifying description: water
and carbon dioxide
are built up
to form
sugars
and other carbohydrates
in the presence
of light
definition: Photosynthesis is the
process by which water and carbon dioxide
are built up to form sugars and
other carbohydrates in the
pre-
sence of light.
Підберить назву процесу в списку зліва
відповідно опису його діяльності в списку справа. Напишіть визначення процесу.
name of process description of course
of action
a)
germination 1)
pollen grains are
transferred from the
stamen to the stigma of the female parts
b)
pollination
2) water passes through the
leaf cells and
evaporates
into the air
c)
transpiration
3) nutrients in the soil pass
through the cell
 membranes into the roof hairs
membranes into the roof hairs
d)
osmosis
4) the seed “ awakens ”
from its dormant
state and starts growing
Завдання № 11.
Заповніть
діаграми, використовуючи слова і вираження надані нижче.
Завдання № 12.
Виберіть правильне вираження часу.
e.g. First the
seed is provided with water, warmth and air, then it starts to
germinate ( after, till, while ).
After
the
seed is provided
with water, warmth and
air, it starts to
germinate.
Перепишіть пропозиції за зразком, обираючи
один із приводів, даних у скобках і поставте їх на початку пропозиції.
Слова, виділені курсивом, опустить.
1.The
young shoot appears above the surface of the ground. Then it begins
the process of photosynthesis ( before, as
soon as, while )
2.
Once
the oxygen has
combined with and
broken down the
various
complex sugars, energy is released ( before,
after, while ).
3.
Dormant seeds are inactive.During
this time they use very little air (when,
before, while).
4.
Once
the shoot appears, the plant then
grows both above and below the
ground ( before, while, after ).
Завдання №13.
Прочитайте та перекладіть текст.
The parts of a plant and their functions
A plant is a
living organism. It is made up of different parts, each of which has a
particular purpose , or specialized function.if one part of the plant is not
functioning properly the whole plant will suffer. But we may cut flowers
off the plant or prune the roots. Such damage is only temporary and
so the plant will continue to grow.
The basic parts of a
plant are the root system , which is bellow the ground, and the shoot system
above. The root of a plant has two main functions. It takes in , or
abcorbs,water and miner als from the soils
through the root hairs,which are single cells hear the tip of each root.
The other main function of the root is to hold or , anchor , the plant in
firmly position in the soil
the shoot system above
the ground consists of the stem , the leaves , the flowers and fruits . one of
the function of the stem is to support the plant . another important function is to enable water and minerals to pass up from the
roots to the leaves and flowers . the leaves make food for the plant by the
process known as photosynthesis . for this process sunlight is necessary .
water from the soil and carbon dioxide
from the air are converted into sugars
and other carbohydrates . during the process oxygen is formed and released into the air .
the flowers contains the reproductive organs of the plant
. the stamens produce the male sex cells . the carpel produces the
female sex cells . the fruit , the
ripened ovary of the flower , encloses the seeds and protects them while they
are developing .
Завдання № 14.
Додайте слова або фрази з тексту , щоб закінчити твердження , що показує вірно або ні ви зрозуміли текст . Зверніть увагу на те ,
що лінія точок потребує фразу , а пряма лінія - слово . Номер указує пропозицію в тексті .
e.g . Each of the different parts of a
plant has a particular purpose . ( 2 )
Each of the different parts of a
plant has a particular purpose or specialized function .
1
. the whole plant will suffer if one part is not …………( 3 )
If all ……… are functioning properly the
whole plant will ______ suffer .
2
. We may ……… off the plant .(4)
This damage ( i.e. cutting flowers ) is
only temporary , the plant ……. .
The whole plant will not
If
we cut flowers off it
3
. a plant has …… , which is below ______
( 6 )
A plant has …… , which is above the
ground .
4
. The root takes in , or _____ , water and minerals from the soil through the root hairs .( 8 )
The root absorbs ……… through the root
hairs .
5
. The roots hold , or -_______ , the plant firmly in position in the soil . (
9)
The plant is anchored firmly in position
in the soil by …… .
Завдання №15.
Перепишіть
пропозиції . замінюючи виділені курсивом вираження з тексту , що мають теж
значення .
e.g.
The roots of plants take in water and
minerals from the soil .
= The roots of plants absorbs water and
minerals from the soil .
1
The single cells near the tip of each
root increase their their surface
area by extending outwards from the root . .
2 .the roots holds the plant firmly in position in the soil .
3
. Sunlight provides the energy for the process of converting water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air into
sugars and other carbonhydrates .
4
.While growing , the seeds are protected by the ripened ovary of the flower .
Завдання № 16.
Позначте на діаграмі частини рослини
дорослої квасолі, використовуючи слова і фрази з тексту.

Завдання № 17.
Дати визначення
різним частинам рослини.
Ми можемо визначити різні частини рослини :
а. / називаючи їх; б
/ установлюючи клас, до якого вони належать;
із / описуючи
їхню функцію.
e.
g. name : root hair
class : parts of a plant
function: absorbs water and
minerals from the soil
Definition : The root hairs are the
parts of the plant which absorbs water and minerals from the soil
Використовуючи
інформацію нижче, дайте повне визначення кожної частини рослини.
a / name : fruit
class :
part of a plant
function: protects the ripened or matured
ovary
b
/ name :
leaves
class :
parts of a plant
function: manufacture sugars and other
carbonhydratesby photosynthesis
c
/ name : root
class
: part of a plant
function: anchors the plant in the soil
and absorbs water and minerals
Завдання № 18.
Досліджуйте такі пропозиції в активному і пасивному заставах.Зверніть увагу на те , що пропозиції в пасиві містять одну з форм дієслова to be і минулий дієприкметник .
A C T I V E
We
improve the fertility of the soil .
P A S S I V E
The
fertility of the soil is improved .
Запишіть дані
пропозиції в пасивній заставі .
1
.Active : The fruit encloses the seeds .
Passive : The seeds ……..by the fruit .
2
.Active : The plant takes in oxygen .
Passive
: Oxygen … … in by the plant .
3
.Active : Wind and insects transfer pollen from one flower to another .
Passive
: Pollen … … by wind and insects
from one flower to another .
4.
Active : The human body requires small quantities of
several minerals.
Passive
: Small quantities of several
minerals …. …. By human body .
5.
Active : Too much cultivation destroys the soil
structure.
Passive
: Soil structure … … by too much
cultivation .
6.
Active :
Soil texture influences all aspects of root development .
Passive :
All aspects of root development …
… by soil texture .
Завдання №19.
Прочитайте
та перекладіть текст.
The origin
and composition of the soil .
The origin and composition of soil .
Soil is a residue of two
main ingredients: mineral material and organic material .Organic material
originates from dead plants and animals and materials other than this are derived from rocks of various kinds . These rocks are broken
down into small particles by
mechanical disintegration and chemical
decomposition . This breaking down process , known as weathering , may thus
both physical and chemical .
When weathering process
are largely physical - by heat or wind ,
for instance – the composition of the soil is very similar to that of the
parent rock . In arid regions weathering is mostly by physical means .But in humid regions chemical
processes of weathering are equally important . In such regions rock particles are affected by water which
may contain carbonic or other weak acid . These acids dissolve some of the particles in the rocks .
The mineral material
that is left behind is insoluble . Consequently , the isoluble mineral residues
in the soil have less resemblance to the original rocks . There are larger
amounts of organic matter in the soil , too .
The process of soil
formation results in the development of the soil profile . This is made up of a
succession of horizontal layers of varying
thickness , from the surface to the parent rock . Generally speaking ,
there are three distinct horizons , known as A , B , and C . A is a top soil ,
which is coarse-grained and dark in colour because of presence of humus .
B is known as a sub-soil
which contains some of the products
leached , or washed , out of the A
horizon . The C horizon consists of parent material which has been weathered in
the upper part , and unweathered rock below .
Any sample of soil
contains particles of different sizes .These have been divided into the
following size groups ;
T A B L E 1
Material
Diameter ( mm )
Gravel
more than 2.0
Coarse-sand 2.0-0.2
Fined sand
0.2-0.02
Silt
0.02-0.002
Clay
less than 0.002
Soils range from pure
clays to pure sands . Most of them
contain various proportions of sand ,
silt and clay and these varyingproportions
make up a soil`s textural class .The principal classes in order of
increasing fineness of material are sand,
loam, silt loam , silty clay loam , clay
loam , silt and clay .
Any soil contains both
mineral and organic matter . Clay particles are the most important of the
mineral particles because they are the smallest .
Smaller sized particles
have a greater exposed surface area than larger sized particles .
Smaller sized particles
can react and combine with water ,nutrients and humus more easily than larger
sized particles .Thus , a clay soil is more reactive than any other type of soil .Humus from decomposed
organic matter is vital to a soil as it
makes a heavy soil lighter .In addition
, it helps to bind the mineral particles together in ‘ crumbs’ .
Завдання № 20.
Додайте слова або фрази з тексту , щоб закінчити твердження , що показує вірно або ні ви зрозуміли текст .
Зверніть увагу на
те , що крапкова лінія потребує фразу , а пряма - слово . Номер указує пропозицію в тексті .
1
. Soil is composed of mineral material and … .( 1)
If the soil material is not organic , it is derived from
… (2)
2
. Rocks of various kinds are … … into small particles (3)
This breaking down process is known as
_________ (4).
3
. In arid regions the weathering process are mostly________ .(6)
4
. In humid regions the water dissolves some of the rocks particles , but leaves behind mineral
materials that is _____ .(10)
5
. The succession of soil horizons makes up the soil ________(13)
Завдання № 21.
Перепишіть такі пропозиції , замінюючи слова , виділені курсивом вираженнями з тексту , що мають теж значення .
1
. Material other than mineral material
is derived from dead plants and animals
.
2
. Breaking down rocks into small
particles is performed mostly by heat or wind in arid or semi-arid
regions .
3
. The remains of mineral materials that
cannot be dissolved in water have
little similarity to
to the parent rocks in humid regions .
4
.The succession of horizontal layers in
a soil are called the top soil , the subsoil
and parent
materials
.
Завдання №22.
Прочитайте опис перетину грунту .
Profile of
soil A : Red Earth
The A horizon extends to a depth of
Horizon
Depth ( cm ) Colour Soil type Structure Other features
A 0 – 36 brownish sandy loam porous and mixed with
Red
friable
pebbles
Granular
B
36 –130 red sandy loam gravely mixed with
Large
Quantities
of
Pebbles
C 130 – 244 yellowish sandy cemented and decomposed
White
compact mass felspars
Прочитайте опис
перетину грунту і складіть таблицю , що надає інформацію , як показано в
прикладі вище .
Profile of Soil : Mountain and hill soil .
The A horizon extends to a depth of
And
some parent material is mixed with the soil . Below
Завдання №23.
Складіть
порівняльні твердження , використовуючи такі шаблони.
Пам'ятаєте , що
порівняльний ступінь двускладних прикметників утворюється при допомозі
закінчення - er , якщо прикметник закінчується на - у , те порівняльна форма
прикметникового має закінчення - ier .
e.g.
Particles of fine sand are coarser than particles of clay .
Вивчіть таблицю : Soil particles Diameter ( mm )
Gravel 2 . 0
or more
Coarse
sand 2 .
0 – 0 .2
Fine
sand 0 . 2- 0 . 02
Silt
0 . 02 – 0 .002
Clay 0
.002 or less
Compare
the particle size of
а ) fine sand with silt ( fine )
b) clay with fine sand (
coarse )
c) fine sand with gravel (
coarse )
a) Soils show great
variations in their sizes and arrangements of their constituent particles. A
sandy soil has larger particles than a
clay soil. A sandy loam has ________ particles than a clay loam.
b) Soils also vary greatly
in colour .A brightly coloured soil indicates a higher degree of oxidation . So
, a red soil has been ______oxidized than a black soil.
a. As agriculture becomes
more intensive , the soil may be
modified by those who form it.A soil can be made less alkaline by adding sulphur. Any soil can
be made ______ acid by adding line .
T a b l e
Top soil Sub –
soil
Colour dark
light
Particle sizes coarse fine
Living organisms many few
Elements for plant food rich
poor
a) colour: 1) The top soil
is …
2) The sub-soil is …
b) particles sizes: 1) The particle sizes of the top soil
…
2) The particle
sizes of the sub-soil …..
с) living organism: 1)There are ……….. in the
top – soil .
2) There are …
… in the sub – soil .
c) elements for plant food
:
1) The
top soil is ………
2) the sub
–soil is … … .
Завдання № 24.
Прочитайте та перекладіть текст.
Manures
and Fertilizers.
Plant growth cannot if
there is not a supply of minerals in a soil. The materials which are available
for this purpose can be divided into two groups: the bulky, organic materials
which are called manures, and the more concentrated, inorganic chemical substances
which are called fertilizers. Farmyard manure, or dung, consists of a mixture
of litter, solid excreta and urine. It contains three most important substances
for plant materials-nitrogen, phosphate and potash. Manure is added to the soil
for several reasons. It improves the physical condition of the soil. It also
keeps up the level of humus in the soil, and maintains the best conditions for
the activities of soil organisms. Finally, it makes up for the plant nutrients
which have been removed by crops or lost by leaching and soil erosion.
Another kind of
manure is green manure. This includes leguminous crops which grow quickly such
as clover and
Fertilizers are usually
classified according to the particular food element which forms their main
constituent. So, they may be grouped as nitrogenous fertilizers, phosphatic
fertilizers, potassic fertilizers and so on.
The most commonly used
fertilizer which contains nitrogen is ammonium sulphate, which is made from
ammonia and sulphuric acid, and which contains 21 % nitrogen. This element
encourages rapid vegetative growth and gives plants a healthy green colour.
Another valuable nitrogenous fertilizer is urea, which is made from ammonia and
carbon dioxide, and contains 46 % nitrogen.
The most widely used
phosphatic fertilizer, super phosphate, is made by treating mineral phosphate
with sulphuric acid. Phosphorous stimulates the formation of a plant,s
roots, and promotes fruit and seed production. Tropical soils are very often
poor in this element.
Finally, wherever high
crop yields are expected, potash is used together with nitrogen and
phosphorous. Potassium makes the plant tissues stronger. This helps the plant
to withstand mechanical damage such as broken branches and torn leaves. In this
way the entry of disease bearing agents, or pathogens, such as bacteria and fungi,
is prevented. Potassium is important for all plants but particularly so for
those that produce oil and starch or sugars. Oil palm and tapioca plants
require potassium in large amounts.
It is usually supplied
in the form of muriate of potash (potassium chloride), which contains 50 to 60
% potassium oxide (K2O) and sulphate of potash (potassium sulphate).
All plants are affected
by the degree of acidity or alkalinity of the soil. The less the nutrient
supply, the more acid the soil becomes. Because mineral salts are basic, an
acid soil has a low base content. Acidity makes some elements unavailable to
plants. If a soil is very acid, with a pH value of less than 5*0, lime can be
added to correct this acidity. The main constituent of lime is calcium, an important
plant food. The presence of lime helps to make essential elements of plant food
more easily available to plants. Nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium are more
easily available in a well-limed soil than in an acid soil.
Завдання № 25.
Додайте слова або фрази з тексту , щоб закінчити
твердження , що показує вірно або ні ви зрозуміли текст.Зверніть увагу , що лінія з точок потребує фразу , а пряма лінія - слово.Номер указує пропозицію в тексті.
1.Two groups of materials are being
compared______and _____.\ 2\
2.Nitrogen ,phosphate and potash
are substances that are found in …….\3\
Farmyard manure contains these three …… substances .\4\
3.There are several reasons why
______is added to the soil .\5\
4.Fertilizers may be grouped as …
…\14\
5.Ammonium sulphate is the mostly
commonly used fertilizer … …\15\
Завдання №26.
Перефразуйте такі пропозиції, використовуючи де можливо слова
і конструкції з тексту.
1.The mostly commonly used
fertilizer which contains nitrogen is made by
combining ammonia with sulphuric
acid .
2.When applied to the soil,the
product which results from treating mineral
phosphate with sulphuric acid promotes the production of fruits and
seeds.
3.Broken branches and torn leaves
allow pathogens such as bakteria and fungi to
enter the plant and destroy it .
4.Essential elements of plant food
are not readily available in a soil with a pH
value of less than 5.0.
Завдання №27.
Спираючись на зразок і використовуючи таблицю, напишіть
пропозиції показавши які симптоми відповідають яким діагнозам.
Mineral deficies
Symptom
Diagnosis
Plant stunted in growth, soil deficient
Leaves yellowish in colour in
nitrogen.
The plant is stunted in growth and
the leaves are yellowish in colour. This shows that the soil is deficient in
nitrogen.
|
Symptom |
Diagnosis |
|
Plant roots dying at tips, or
remain short and stubby |
Sulphur deficiency in soil. |
|
Plant tissues weak, prone to
attack by insects and fungus |
Soil deficient in potassium |
|
Leaves losing their green colour,
become yellow at tips, between veins |
Deficiency of phosphorous |
|
New leaves turning yellow, roots
and stems becoming long and woody |
Supply of calcium in soil is low |
Завдання № 28.
Означальні підрядні пропозиції / Attributive
clauses / виконують у складній пропозиції функцію визначення і відповідають на питання What?
Which ? і з'єднуються з головною пропозицією союзними словами who? , whose? ,
which? і прислівниками when? , where?
,why?
e.g. Fertilizers why?h have nitrogen as the main food element
are called nitrogenous fertilizers.
Об'єднаєте кожну пару пропозицій в одну, перетворивши другу
пропозицію в підрядне.
Ammonium sulphate……. Is
the most commonly used nitrogenous fertilizer. Ammonium sulphate supplies the
soil with nitrogen and sulphur.
2.A compost is a mixture of partly broken down material…… This material
is usually made up of grass cuttings.
3.A leguminous crop….. will add as
much nitrogen to the soil per acre as 3 to 10 tons of farmyard manure. A
leguminous crop is ploughed under
Завдання № 29.
Означальні підрядні часто вживаються в скороченій формі:
У підрядних, що починаються which has or which have,
може бути використаний привід С.
e. g. Rice
varieties which have short erect leaves
respond well to high levels of fertilizer.
= Rice varieties with short erect leaves respond well to
high levels of fertilizer.
У підрядних, де замість активної форми дієслова може бути
застосована -
ing форма.
e.g. Rice varieties which have short erect leaves respond
well to high levels of fertilizer.
= Rice varieties having short erect leaves respond well
to high levels of fertilizer.
The most commonly used fertilizer which contains nitrogen is ammonium
sulphare.
= The most commonly used fertilizer
containing nitrogen is ammonium
sulphare.
У підрядних пропозиціях, у яких дієслово в пасивній формі,
відносний займенник і форма дієслова to be не застосовуються.
e.g. The guantity of fertilizer or
manure which is reguired for rice
cultivation partly depends on the variety of rice which is used.
= . The guantity of fertilizer or manure required
for rice cultivation partly depends on the variety of rice which is used.
У підрядних пропозиціях, де за відносним займенником випливає форма дієслова to be і визначення або іменник , відносний займенник і форма дієслова to be можуть не застосовуватися.
e.g. Common nitrogen fertilizer which are suitable for rice are ammonium
sulphare and urea.
= Common nitrogen fertilizer suitable for rice are ammonium sulphare
and urea.
Urea, which is the substance in human an urine, is a nitrogenous
fertilizer.
= Urea, the substance in human an urine, is a nitrogenous fertilizer
Об'єднаєте кожну пару пропозицій в одну, змінюючи другу
пропозицію в стислу форму підрядної пропозиції і підставте в першу пропозицію
замість крапок.
Muriate of potash is a form of
potash…… This form of potash is used in
many compound fertilizers.
1.Viruses are very small
organisms………
They are usually transmitted by
means of insects.
2.Nematodes are small worms in the
soil that enter plant roots…..
They cause serious losses in some
crops, particularly in the tropics.
3.Compond fertilizers are multiple
nutrient materials……
They supply two or three plant
nutrient simultaneously.
4.It is essential to understand the
materials…..
The materials are available to the
farmer to maintain the supply of minerals in the soil.
Словник
|
Acid
Acid soil Available Apply On account Arid region |
Кислота Кислотні грунти Доступний Застосуватися В рахунок чого-небудь Марна(посушлива) область(регіон) |
|
Blast bear bore, borne| |
Хвороба рослини Приносить плоди |
|
Carbon dioxide Carbon hydrates Conversion Cycle
Coarse sand Clay loam
Crumb
Canker
Cell
Carbonic |
Вуглекислий газ
Вуглеводень Перетворення Цикл Зернистий пісок Масна глина Крихітка Рак (наріст) Клітина Вуглецевий |
|
Decay Destroy Dissolve Dung Dust Disease Damage Derive Dormant |
Відмирати Руйнувати Розчиняти Гній (добриво) Пилюка Хвороба Ушкодження Відбуватися
(від) Сплячий |
|
Evolve |
Розвивати
(тися) |
|
Fertile Fertilization Fine sand Farmyard manure
Fungi
foliage fungus
fleshy
fertilizer
|
Родючий Запліднення Дрібний пісок Органічне
добриво Гриб
(наріст) Гриб Гриб М'ясистий Добриво |
|
Germination Growth
Gravel Grafts
To get rid of |
Проріст Ріст Гравій Щеплення Звільнятися |
|
host harmful humid
|
Організм, що
харчує паразитів Шкідливий Вологий |
|
Insoluble Infection Invasive |
Нерозчинний Інфекція Агресивний |
|
Keep up |
Підтримувати, зберігати |
|
Loamy sand Loam Leaching Lime
|
Супісок Глина масна Вищелащивання Вапняк |
|
moisture manufacture mature maintain |
Вологість Робити Доросле Зберігати |
|
Occur oxygen |
Відбуватися
Кисень |
|
Nutrient nitrogen |
Корисний Азот |
|
Pollination Property Phosphate |
Запилення Власність Фосфат |
|
root ripen
reproductive
reduce
residues resistant remove |
Корінь Зрілий Репродуктивний Скорочувати Осадок Наполегливий Видаляти |
|
Seed
Spread Sub-soil Silt Sickly Supply Substance Spray Soil-borne
disease Stamen Stem |
Розщеплення Зерно, насіння Поширювати Підгрунтовий
прошарок Мул Хворобливий Забезпечувати Речовина Обприскувати Грунтова
хвороба Тичинка Стебло |
|
Treat |
Гоїти |
|
Vapour |
Пар (пароподібний) |
|
Well-drained soils weed |
Дренажні грунти Бур'ян |